12 English Tenses : Formulas, Rules with Examples
In this guide, we will explore the 12 English tenses, providing clear formulas, rules, and practical examples to help you grasp each tense with confidence. Go slowly and you will get what you need for your exams, to improve your writing or simply to speak more fluently. Dive into the details and elevate your English proficiency with our simple guide! Plus, don’t forget to download your free English Tenses Formula PDF at the end of this article to have a handy reference at your fingertips!
What are the 12 Different English Tenses ?
The three main verb tenses are past, present, and future, and each tense is further divided into four grammatical aspects: simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous.
All English Tenses Formula
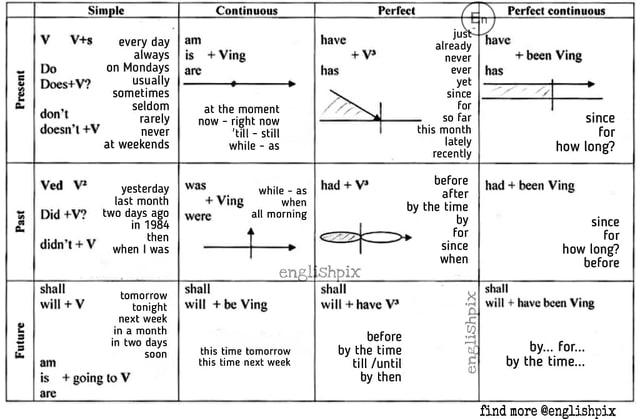
1. Present Tense
The Present Tense describes actions that are currently happening, habits, or general truths.
a. Simple Present
- Usage: Describes habitual actions, universal truths, and scheduled events.
- Examples:
- Affirmative: She writes a letter.
- Negative: She does not write a letter.
- Question: Does she write a letter?
Structure:
- Affirmative: Subject + base verb (+ s/es) + object
- Negative: Subject + does not + base verb + object
- Question: Does + subject + base verb + object?
- Negative Question: Does + subject + not + base verb + object?
b. Present Continuous
- Usage: Indicates actions happening at the moment of speaking or temporary situations.
- Examples:
- Affirmative: She is writing a letter.
- Negative: She is not writing a letter.
- Question: Is she writing a letter?
Structure:
- Affirmative: Subject + is/am/are + base verb + ing + object
- Negative: Subject + is/am/are + not + base verb + ing + object
- Question: Is/am/are + subject + base verb + ing + object?
- Negative Question: Is/am/are + subject + not + base verb + ing + object?
c. Present Perfect
- Usage: Describes actions that started in the past and have relevance to the present.
- Examples:
- Affirmative: She has written a letter.
- Negative: She has not written a letter.
- Question: Has she written a letter?
Structure:
- Affirmative: Subject + has/have + past participle (V3) + object
- Negative: Subject + has/have + not + past participle (V3) + object
- Question: Has/have + subject + past participle (V3) + object?
- Negative Question: Has/have + subject + not + past participle (V3) + object?
d. Present Perfect Continuous
- Usage: Highlights the duration of an action that began in the past and is still ongoing.
- Examples:
- Affirmative: She has been writing a letter.
- Negative: She has not been writing a letter.
- Question: Has she been writing a letter?
Structure:
- Affirmative: Subject + has/have + been + base verb + ing + object
- Negative: Subject + has/have + not + been + base verb + ing + object
- Question: Has/have + subject + been + base verb + ing + object?
- Negative Question: Has/have + subject + not + been + base verb + ing + object?
2. Past Tense
The Past Tense is used to describe actions that have already happened.
a. Simple Past
- Usage: Describes actions completed in the past or past habits.
- Examples:
- Affirmative: She wrote a letter.
- Negative: She did not write a letter.
- Question: Did she write a letter?
Structure:
- Affirmative: Subject + past verb (V2) + object
- Negative: Subject + did not + base verb + object
- Question: Did + subject + base verb + object?
- Negative Question: Did + subject + not + base verb + object?
b. Past Continuous
- Usage: Indicates an action that was ongoing at a specific time in the past.
- Examples:
- Affirmative: She was writing a letter.
- Negative: She was not writing a letter.
- Question: Was she writing a letter?
Structure:
- Affirmative: Subject + was/were + base verb + ing + object
- Negative: Subject + was/were + not + base verb + ing + object
- Question: Was/were + subject + base verb + ing + object?
- Negative Question: Was/were + subject + not + base verb + ing + object?
c. Past Perfect
- Usage: Describes an action that was completed before another action in the past.
- Examples:
- Affirmative: She had written a letter before he arrived.
- Negative: She had not written a letter.
- Question: Had she written a letter?
Structure:
- Affirmative: Subject + had + past participle (V3) + object
- Negative: Subject + had + not + past participle (V3) + object
- Question: Had + subject + past participle (V3) + object?
- Negative Question: Had + subject + not + past participle (V3) + object?
d. Past Perfect Continuous
- Usage: Describes an action that started in the past and continued until another past action.
- Examples:
- Affirmative: She had been writing a letter for an hour before he arrived.
- Negative: She had not been writing a letter.
- Question: Had she been writing a letter?
Structure:
- Affirmative: Subject + had + been + base verb + ing + object
- Negative: Subject + had + not + been + base verb + ing + object
- Question: Had + subject + been + base verb + ing + object?
- Negative Question: Had + subject + not + been + base verb + ing + object?
3. Future Tense
The Future Tense is used to describe actions that have not yet happened but will happen in the future.
a. Simple Future
- Usage: Describes an action that will occur in the future.
- Examples:
- Affirmative: She will write a letter.
- Negative: She will not write a letter.
- Question: Will she write a letter?
Structure:
- Affirmative: Subject + will/shall + base verb + object
- Negative: Subject + will/shall + not + base verb + object
- Question: Will/shall + subject + base verb + object?
- Negative Question: Will/shall + subject + not + base verb + object?
b. Future Continuous
- Usage: Indicates an action that will be ongoing at a specific time in the future.
- Examples:
- Affirmative: She will be writing a letter at 5 PM tomorrow.
- Negative: She will not be writing a letter.
- Question: Will she be writing a letter?
Structure:
- Affirmative: Subject + will/shall + be + base verb + ing + object
- Negative: Subject + will/shall + not + be + base verb + ing + object
- Question: Will/shall + subject + be + base verb + ing + object?
- Negative Question: Will/shall + subject + not + be + base verb + ing + object?
c. Future Perfect
- Usage: Describes an action that will be completed before a certain point in the future.
- Examples:
- Affirmative: She will have written a letter by tomorrow.
- Negative: She will not have written a letter.
- Question: Will she have written a letter?
Structure:
- Affirmative: Subject + will/shall + have + past participle (V3) + object
- Negative: Subject + will/shall + not + have + past participle (V3) + object
- Question: Will/shall + subject + have + past participle (V3) + object?
- Negative Question: Will/shall + subject + not + have + past participle (V3) + object?
d. Future Perfect Continuous
- Usage: Describes an action that will be ongoing up until a specific time in the future.
- Examples:
- Affirmative: She will have been writing a letter for two hours by the time he arrives.
- Negative: She will not have been writing a letter.
- Question: Will she have been writing a letter?
Structure:
- Affirmative: Subject + will/shall + have been + base verb + ing + object
- Negative: Subject + will/shall + not + have been + base verb + ing + object
- Question: Will/shall + subject + have been + base verb + ing + object?
- Negative Question: Will/shall + subject + not + have been + base verb + ing + object?



