Basic Helping Verbs Guide: Was vs. Were, Has vs. Have & More
Mastering the basic auxiliary verbs is essential for ESL students and English learners. This lesson will enable you to understand the basic helping verb (auxiliary verb) groups: is/are/am, do/does, was/were, and has/have, as these verbs are fundamental in constructing sentences to be used in different tenses and contexts.
This article will help you understand the difference between four basic helping verb groups: is/are/am, do/does, was/were, and has/have. These basic helping verbs are important for constructing sentences in different tenses and contexts.
1. How to Use: Am – Is – Are
These verbs are forms of the verb “to be” and are used in the present tense. Their usage depends on the subject:
- I am
- You are
- He/She/It is
- We are
- They are
Here are example sentences using am, is, are with all pronouns in positive, negative, and question forms.
I
I am a student.
I am not hungry.
Am I late?
You
You are my best friend.
You are not tired. (or: You aren’t tired.)
Are you ready?
He
He is a good singer.
He is not at home. (or: He isn’t at home.)
Is he coming with us?
She
She is very kind.
She is not in the office today. (or: She isn’t in the office.)
Is she your sister?
It
It is a sunny day.
It is not cold outside. (or: It isn’t cold outside.)
Is it raining?
We
We are happy.
We are not going to the park. (or: We aren’t going.)
Are we on the right bus?
You (plural)
You are my classmates.
You are not late. (or: You aren’t late.)
Are you enjoying the movie?
They
They are in the garden.
They are not at work. (or: They aren’t at work.)
Are they coming to the party?

2. How to Use: Do/Does
“Do” and “does” are auxiliary verbs used in the present tense for questions, negatives, and emphatic sentences. “Does” is used with singular third-person subjects (he, she, it), while “do” is used with all other subjects.
- I/You/We/They do
- He/She/It does
Here are example sentences using do and does with all pronouns in positive, negative, and question forms.
1. I
I do my best in school.
I do not eat meat. (or: I don’t eat meat.)
Do I need to bring my book?
2. You
You do great work.
You do not need help. (or: You don’t need help.)
Do you like reading?
3. We
We do our homework on time.
We do not watch horror movies. (or: We don’t watch horror movies.)
Do we have a test tomorrow?
4. They
They do their jobs well.
They do not go to the gym. (or: They don’t go to the gym.)
Do they speak English?
5. He
He does his homework every day.
He does not like coffee. (or: He doesn’t like coffee.)
Does he play football?
6. She
She does her job well.
She does not watch TV. (or: She doesn’t watch TV.)
Does she live near here?
7. It
It does make a difference.
It does not work properly. (or: It doesn’t work properly.)
Does it taste good?

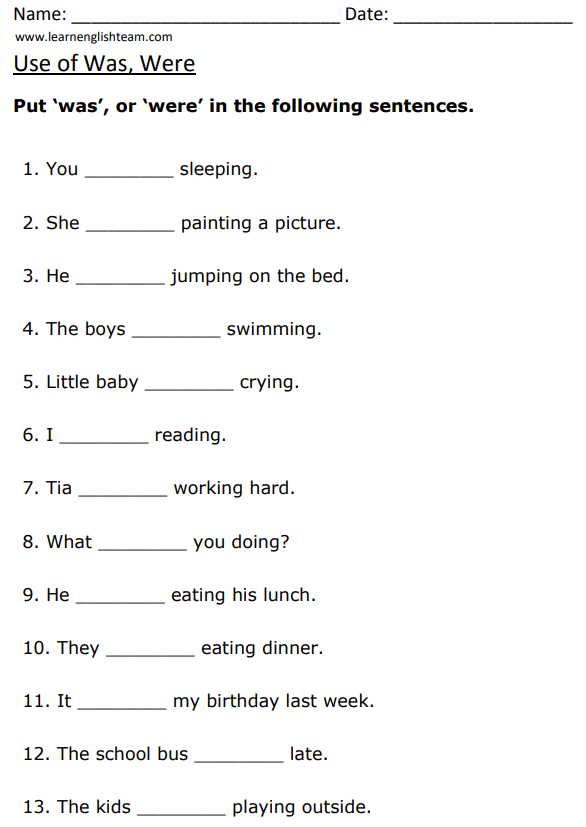
3. How to Use: Was/Were
“Was” and “were” are past tense forms of the verb “to be.” Use “was” with singular subjects (except “you”) and “were” with plural subjects and “you.”
- I/He/She/It was
- You/We/They were
Here are example sentences using was and were with all pronouns in positive, negative, and question forms:
I
I was at the party yesterday.
I was not feeling well. (or: I wasn’t feeling well.)
Was I late for the meeting?
He
He was a great athlete in school.
He was not happy with the results. (or: He wasn’t happy.)
Was he at the event?
She
She was my teacher last year.
She was not at work yesterday. (or: She wasn’t at work.)
Was she surprised by the news?
It
It was a wonderful experience.
It was not easy to finish the project. (or: It wasn’t easy.)
Was it your idea?
We
We were at the beach all day.
We were not able to attend the meeting. (or: We weren’t able.)
Were we supposed to bring our laptops?
You (plural)
You were all great during the presentation.
You were not here earlier. (or: You weren’t here.)
Were you at the concert last night?
They
They were happy with the results.
They were not interested in the proposal. (or: They weren’t interested.)
Were they excited about the trip?
4. How to Use: Has/Have
“Has” and “have” are forms of the verb “to have” and are used in the present tense. “Has” is used with singular third-person subjects, while “have” is used with all other subjects.
- I/You/We/They have
- He/She/It has
Here are example sentences using have and has with all pronouns in positive, negative, and question forms:
I
I have finished my homework.
I have not seen that movie. (or: I haven’t seen that movie.)
Have I missed anything?
He
He has a new car.
He has not completed the project. (or: He hasn’t completed the project.)
Has he arrived yet?
She
She has a lot of friends.
She has not been to Paris. (or: She hasn’t been to Paris.)
Has she left already?
It
It has been raining all day.
It has not been an easy task. (or: It hasn’t been easy.)
Has it stopped snowing?
Plural & “You/I” Pronouns (Use “have”)
I
I have seen that movie before.
I have not heard from her. (or: I haven’t heard from her.)
Have I done something wrong?
You
You have a beautiful voice.
You have not finished your work yet. (or: You haven’t finished your work yet.)
Have you been to the new restaurant?
We
We have visited that place many times.
We have not made a decision yet. (or: We haven’t made a decision yet.)
Have we received the package?
They
They have completed the assignment.
They have not spoken to me. (or: They haven’t spoken to me.)
Have they left the office already?
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Mixing up singular and plural forms:
- Incorrect: She do her homework.
- Correct: She does her homework.
- Using “was” instead of “were” with plural subjects:
- Incorrect: They was happy.
- Correct: They were happy.
- Forgetting the correct verb form for “has” and “have”:
- Incorrect: He have a car.
- Correct: He has a car.
Summary Table
| Verb Group | Singular | Plural |
|---|---|---|
| Is/Are/Am | I am, He/She/It is | We/You/They are |
| Do/Does | He/She/It does | I/We/You/They do |
| Was/Were | I/He/She/It was | We/You/They were |
| Has/Have | He/She/It has | I/We/You/They have |
Practice Exercises
- Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb:
- She … (is/are) a teacher.
- They … (do/does) their chores every morning.
- I … (was/were) at home last night.
- He … (has/have) a pet dog.
- Rewrite the following sentences correctly:
- He do not like apples.
- You was late for the meeting.
- They has a big house.